




|
|
A minimally invasive procedure on a joint using a ‘key-hole’ approach and small camera (an ‘arthroscope’) and special instruments to examine and treat a joint.
Affecting both sides (i.e. the left and the right). Usually described as ‘bilateral forelimb lameness’ (both front legs are affected) or ‘bilateral hind limb lameness’ (both hind legs are affected).
See osteochondral fragment.
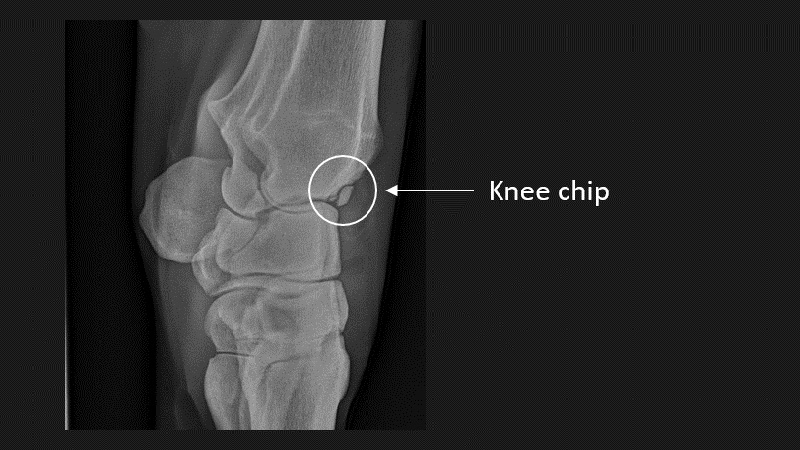
An individual bone of the horse’s knee joint (the carpus), which is equivalent to the human wrist.
Persisting for a long time or constantly recurring.
Colic is a common name for abdominal pain. Colic surgery in the horse often involves correcting intestinal twists and obstructions.
Inflammation of a ligament.
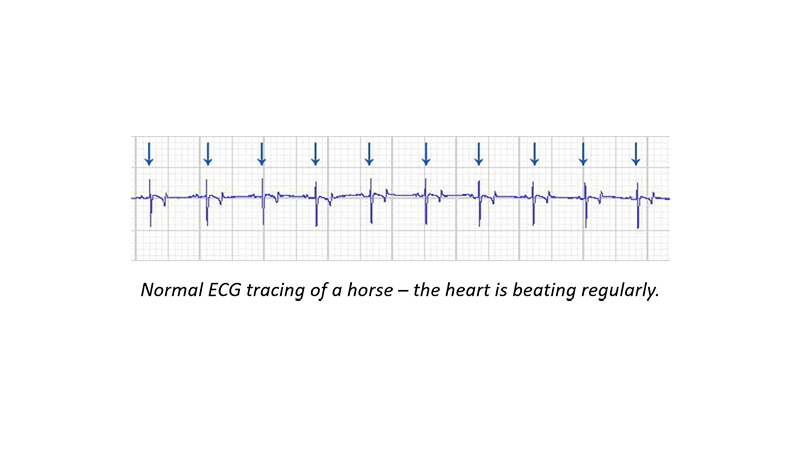
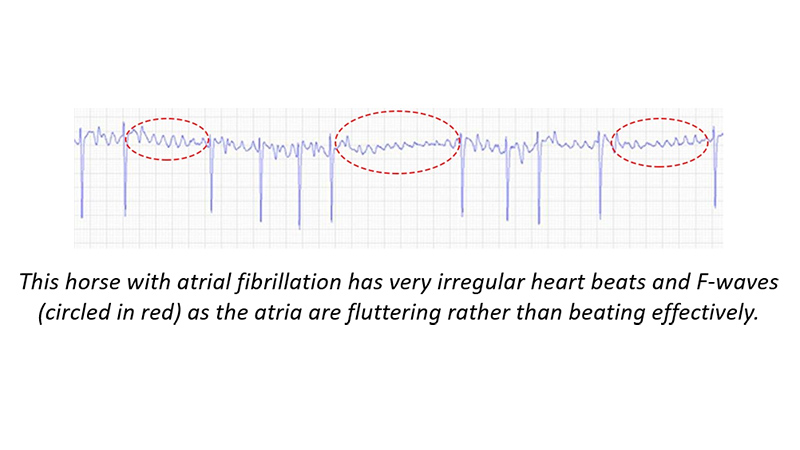
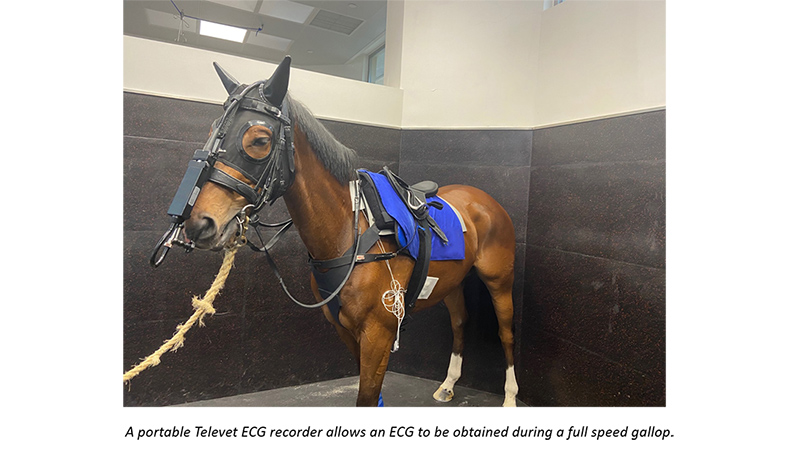
An examination performed to measure and record the electrical activity of the heart and to diagnose cardiac arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms) that may affect the health and / or racing performance of a horse, for example, atrial fibrillation.
A blood-filled swelling often caused by trauma with rupture of blood vessels and bleeding into tissues, for example in muscle tissue or under the skin.
An abnormal heart rhythm. Sometimes detected during a post-race veterinary inspection of a horse and which may have affected the racing performance of that horse. The most common abnormal heart irregularity in racehorses is atrial fibrillation.
--red-spot-with-an-arrow.jpg)
An increased volume of fluid within a joint which is usually caused by injury and inflammation of joint structures.
Heat, pain and swelling of a joint often causing the production of watery joint fluid that does not lubricate and protect joint surfaces as well as healthy joint fluid.
Lameness is an abnormal way of locomotion caused by the horse trying to relieve musculoskeletal pain and / or protect an injured structure during movement. It is usually graded in severity from grade 0 (normal) to 5 (unable to bear weight on the limb).
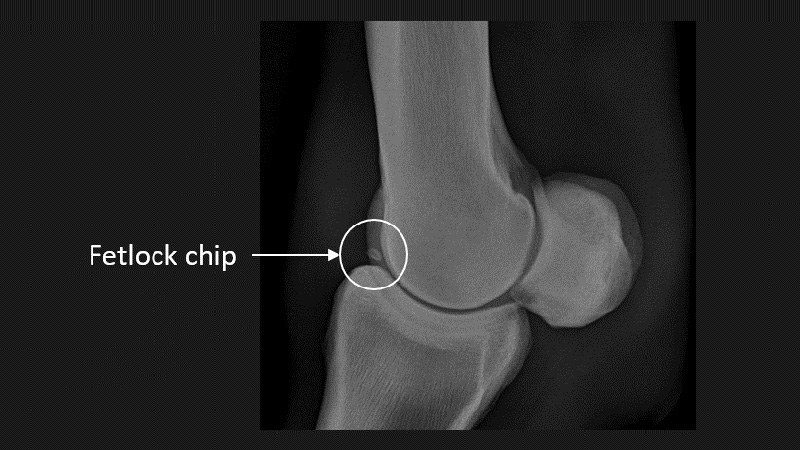
A ‘chip’ of bone and cartilage (hence ‘osteochondral’) that has broken off within a joint, usually from its margin. Joints most commonly affected in race horses are the fetlock and the carpus (knee). Surgical removal of osteochondral fragments via keyhole arthroscopic surgery is often recommended.
An ongoing process of bone turnover, where bone tissue is removed and replaced with new bone in a process that takes around 3 months. The process of bone remodelling is suppressed during intense race training permitting microdamage to accumulate. Periods of rest from race training (for around 3 months) are needed to allow for the replacement of damaged bone with new bone.
Pain emanating from the front of the cannon bones, most commonly in the front limbs, and commonly occurring in horses in their first year of race training. Occasionally progresses to a stress fracture.
Fluid filled structure surrounding some of the tendons in the limbs that lubricate the tendons and ease their passage around a bend in the limb.
The common throat conditions that may affect breathing during exercise and require surgical correction include laryngeal hemiplegia, Dorsal Displacement of the Soft Palate (DDSP) and epiglottic entrapment.